Difference between revisions of "Driven oscillations of a mass on a nonlinear spring"
From Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[ru:Нелинейные колебания груза с вынуждающей силой]] |
| + | [[File:Nolinekoleban2.png|thumb|Driven oscillations of a mass on a nonlinear spring|500px]] | ||
== Annotation to the project == | == Annotation to the project == | ||
| − | This project gives an idea about nonlinear oscillation of | + | This project gives an idea about nonlinear oscillation of a mass with the periodic force acting on it. |
== Formulation of the problem == | == Formulation of the problem == | ||
| − | Let’s put that | + | Let’s put that a mass on nonlinear spring has mass m and experiencing the action of an external force F, which has a law F = sin (t). |
| − | * Task: formulate the problem on JavaScript which modulate motion of | + | * Task: formulate the problem on JavaScript which modulate motion of a mass with different parameters of the system.<br> |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | If the periodically changing external force is acting on the system, the system performs oscillations which repeat | + | If the periodically changing of the external force is acting on the system, the system performs oscillations which repeat the pattern of changes of this force. Such oscillations are '''called forced'''. |
F0 is the force amplitude and the greatest value of the force. | F0 is the force amplitude and the greatest value of the force. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Because of the work of an external force, the maximum value of the potential energy of the spring and the kinetic energy of | + | | Because of the work of an external force, the maximum value of the potential energy of the spring and the kinetic energy of a mass increase. This will increase the loss on overcome the resistance forces. In the end the work of the external force will exactly offset the energy losses in the system. Further growth of the oscillations in the system will stop and oscillations will be established with a constant amplitude. || [[File:123.png|thumb|A typical plot of the amplitude function]] |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
{{#widget:Iframe |url=http://tm.spbstu.ru/htmlets/Kiselev/Spring/Springs.html |width=800 |height=800 |border=0 }} | {{#widget:Iframe |url=http://tm.spbstu.ru/htmlets/Kiselev/Spring/Springs.html |width=800 |height=800 |border=0 }} | ||
| − | Download program: [[ | + | Download program: [[Media:SpringNoLine.rar|SpringNoLine.rar]] |
| − | '''Text of the program on JavaScript (creator | + | <!--'''Text of the program on JavaScript (creator Pavel Kiselev):''' <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> |
File '''"Spring.js"''' | File '''"Spring.js"''' | ||
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang="javascript" enclose="div"> | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="javascript" enclose="div">--> |
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:100%" > | |
| + | '''The Text of the program is written in JavaScript (developed by Pavel Kiselev):''' <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | window.addEventListener("load", Main_Spring, true); | ||
function Main_Spring() { | function Main_Spring() { | ||
var canvas = spring_canvas; | var canvas = spring_canvas; | ||
| − | canvas.onselectstart = function () {return false;}; // prohibition selection canvas | + | canvas.onselectstart = function () {return false;}; // prohibition of selection canvas |
| − | var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); // at the ctx | + | var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); // drawing at the ctx |
var w = canvas.width; // the width of the window in the calculated coordinates | var w = canvas.width; // the width of the window in the calculated coordinates | ||
var h = canvas.height; // the height of the window in the calculated coordinates | var h = canvas.height; // the height of the window in the calculated coordinates | ||
| − | var Pi = 3.1415926; | + | var Pi = 3.1415926; // Pi |
| − | var m0 = 1; | + | var m0 = 1; // weight scale |
| − | var T0 = 1; | + | var T0 = 1; // time scale (the period of oscillation of the original system) |
var t = 0; | var t = 0; | ||
| − | var k0 = 2 * Pi / T0; | + | var k0 = 2 * Pi / T0; // frequency scale |
| − | var C0 = m0 * k0 * k0; | + | var C0 = m0 * k0 * k0; // hardness scale |
| − | var B0 = 2 * m0 * k0; | + | var B0 = 2 * m0 * k0; // viscosity scale |
var omega = 10; | var omega = 10; | ||
| − | // *** Creating the physical parameters*** | + | // *** Creating the physical parameters *** |
var F = 80; | var F = 80; | ||
| − | var m = 1 * m0; | + | var m = 1 * m0; // weight |
| − | var C = 1 * C0; | + | var C = 1 * C0; // rigidity |
| − | var C1 = 1 * C0; | + | var C1 = 1 * C0; // rigidity1 |
| − | var B = .1 * B0; | + | var B = .1 * B0; // viscosity |
slider_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1); number_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1); | slider_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1); number_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1); | ||
| Line 61: | Line 65: | ||
slider_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1); number_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1); | slider_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1); number_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1); | ||
| − | // *** Creating the parameters | + | // *** Creating the computing parameters *** |
| − | var fps = 300; | + | var fps = 300; // frames per second |
| − | var spf = 100; | + | var spf = 100; // steps per frame |
| − | var dt = 0.05 * T0 / fps; | + | var dt = 0.05 * T0 / fps; // integration step (calculation quality) |
var steps = 0; // the number of integration steps | var steps = 0; // the number of integration steps | ||
| Line 86: | Line 90: | ||
var count = true; // system analysis | var count = true; // system analysis | ||
| − | var v = 0; | + | var v = 0; // speed of a mass |
| − | var rw = canvas.width / 30; | + | var rw = canvas.width / 30; |
var rh = canvas.height / 1.5; | var rh = canvas.height / 1.5; | ||
| − | var x0 = 15 * rw - rw / 2; | + | var x0 = 15 * rw - rw / 2; |
var y0 = rh / 1.33 - rh / 2; | var y0 = rh / 1.33 - rh / 2; | ||
| Line 97: | Line 101: | ||
var startX = 0; // spring fastening | var startX = 0; // spring fastening | ||
| − | // create a rectangle | + | // create a rectangle (mass) |
var rect = { | var rect = { | ||
x: x0, width: rw, | x: x0, width: rw, | ||
| − | y: y0, height: rh, | + | y: y0, height: rh, |
| − | fill: "rgba(0, 0, 255, 1)" | + | fill: "rgba(0, 0, 255, 1)" // colour |
}; | }; | ||
| Line 108: | Line 112: | ||
document.onmousedown = function(e) { // function by pressing the mouse button | document.onmousedown = function(e) { // function by pressing the mouse button | ||
var m = mouseCoords(e); // we get estimated coordinates of the mouse cursor | var m = mouseCoords(e); // we get estimated coordinates of the mouse cursor | ||
| + | |||
var x = rect.x; | var x = rect.x; | ||
var xw = rect.x + rect.width; | var xw = rect.x + rect.width; | ||
| Line 123: | Line 128: | ||
}; | }; | ||
| − | document.onmouseup = function(e) { | + | document.onmouseup = function(e) { // function when you release the mouse button |
| − | + | document.onmousemove = null; // when the key is released, no movement function | |
count = true; | count = true; | ||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 144: | Line 149: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | // plot | + | // plot |
var vGraph = new TM_graph( // determine the plot | var vGraph = new TM_graph( // determine the plot | ||
"#vGraph", // on html-element #vGraph | "#vGraph", // on html-element #vGraph | ||
250, // the number of steps by "x" axis | 250, // the number of steps by "x" axis | ||
| − | -1, 1, 0.2); // min value of Y-axis, max value of Y-axis, Y-axis step | + | -1, 1, 0.2); // min value of Y-axis, max value of Y-axis, Y-axis step |
function control() { | function control() { | ||
| Line 155: | Line 160: | ||
requestAnimationFrame(control); | requestAnimationFrame(control); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | control() | + | control() |
// setInterval(control, 1000 / fps); // start of the system | // setInterval(control, 1000 / fps); // start of the system | ||
| Line 162: | Line 167: | ||
for (var s=1; s<=spf; s++) { | for (var s=1; s<=spf; s++) { | ||
var f = -B*v - C * (rect.x - x0) - C1*Math.pow(rect.x - x0,3)+2*F*Math.sin(t); | var f = -B*v - C * (rect.x - x0) - C1*Math.pow(rect.x - x0,3)+2*F*Math.sin(t); | ||
| − | + | v += f / m * dt; | |
| − | + | //console.log(f); | |
rect.x += v * dt; | rect.x += v * dt; | ||
| − | + | t+= dt; | |
steps++; | steps++; | ||
if (steps % 80 == 0) vGraph.graphIter(steps, (rect.x-x0)/canvas.width*2); // infeed graph data | if (steps % 80 == 0) vGraph.graphIter(steps, (rect.x-x0)/canvas.width*2); // infeed graph data | ||
| Line 174: | Line 179: | ||
function draw() { | function draw() { | ||
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, w, h); | ctx.clearRect(0, 0, w, h); | ||
| − | + | draw_spring(startX, rect.x, h/2, 10, 50); | |
ctx.fillStyle = "#0000ff"; | ctx.fillStyle = "#0000ff"; | ||
ctx.fillRect(rect.x, rect.y, rect.width, rect.height); | ctx.fillRect(rect.x, rect.y, rect.width, rect.height); | ||
| Line 180: | Line 185: | ||
| − | + | function draw_spring(x_start, x_end, y, n, h) { | |
| − | + | ctx.lineWidth = 2; | |
ctx.strokeStyle = "#7394cb"; | ctx.strokeStyle = "#7394cb"; | ||
| − | + | var L = x_end - x_start; | |
| − | + | for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |
| − | + | var x_st = x_start + L / n * i; | |
| − | + | var x_end = x_start + L / n * (i + 1); | |
| − | + | var l = x_end - x_st; | |
| − | + | ctx.beginPath(); | |
| − | + | ctx.bezierCurveTo(x_st, y, x_st + l / 4, y + h, x_st + l / 2, y); | |
| − | + | ctx.bezierCurveTo(x_st + l / 2, y, x_st + 3 * l / 4, y - h, x_st + l, y); | |
| − | + | ctx.stroke(); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | } | |
} | } | ||
Latest revision as of 18:35, 18 January 2017
Contents
Annotation to the project[edit]
This project gives an idea about nonlinear oscillation of a mass with the periodic force acting on it.
Formulation of the problem[edit]
Let’s put that a mass on nonlinear spring has mass m and experiencing the action of an external force F, which has a law F = sin (t).
- Task: formulate the problem on JavaScript which modulate motion of a mass with different parameters of the system.
Overview[edit]
If the periodically changing of the external force is acting on the system, the system performs oscillations which repeat the pattern of changes of this force. Such oscillations are called forced.
F0 is the force amplitude and the greatest value of the force.
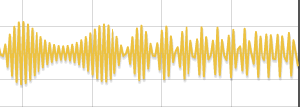
| Because of the work of an external force, the maximum value of the potential energy of the spring and the kinetic energy of a mass increase. This will increase the loss on overcome the resistance forces. In the end the work of the external force will exactly offset the energy losses in the system. Further growth of the oscillations in the system will stop and oscillations will be established with a constant amplitude. |
Equation of motion:
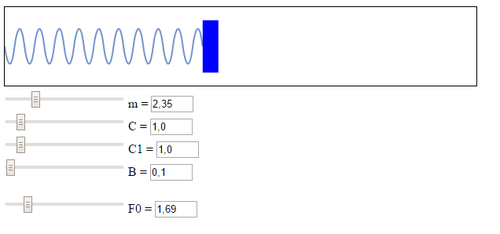
Visualization on JavaScript[edit]
Download program: SpringNoLine.rar
The Text of the program is written in JavaScript (developed by Pavel Kiselev):
window.addEventListener("load", Main_Spring, true);
function Main_Spring() {
var canvas = spring_canvas;
canvas.onselectstart = function () {return false;}; // prohibition of selection canvas
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d"); // drawing at the ctx
var w = canvas.width; // the width of the window in the calculated coordinates
var h = canvas.height; // the height of the window in the calculated coordinates
var Pi = 3.1415926; // Pi
var m0 = 1; // weight scale
var T0 = 1; // time scale (the period of oscillation of the original system)
var t = 0;
var k0 = 2 * Pi / T0; // frequency scale
var C0 = m0 * k0 * k0; // hardness scale
var B0 = 2 * m0 * k0; // viscosity scale
var omega = 10;
// *** Creating the physical parameters ***
var F = 80;
var m = 1 * m0; // weight
var C = 1 * C0; // rigidity
var C1 = 1 * C0; // rigidity1
var B = .1 * B0; // viscosity
slider_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1); number_m.value = (m / m0).toFixed(1);
slider_C.value = (C / C0).toFixed(1); number_C.value = (C / C0).toFixed(1);
slider_C1.value = (C / C0).toFixed(1); number_C1.value = (C / C0).toFixed(1);
slider_B.value = (B / B0).toFixed(1); number_B.value = (B / B0).toFixed(1);
slider_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1); number_F.value = (F / 40).toFixed(1);
// *** Creating the computing parameters ***
var fps = 300; // frames per second var spf = 100; // steps per frame var dt = 0.05 * T0 / fps; // integration step (calculation quality) var steps = 0; // the number of integration steps
function setM(new_m) {m = new_m * m0;}
function setC(new_C) {C = new_C * C0;}
function setC1(new_C1) {C1 = new_C1 * C0 * 0.067;}
function setB(new_B) {B = new_B * B0;}
function setF(new_F) {F = new_F * 40;}
slider_m.oninput = function() {number_m.value = slider_m.value; setM(slider_m.value);};
number_m.oninput = function() {slider_m.value = number_m.value; setM(number_m.value);};
slider_C.oninput = function() {number_C.value = slider_C.value; setC(slider_C.value);};
number_C.oninput = function() {slider_C.value = number_C.value; setC(number_C.value);};
slider_C1.oninput = function() {number_C1.value = slider_C1.value; setC1(slider_C1.value);};
number_C1.oninput = function() {slider_C1.value = number_C1.value; setC1(number_C1.value);};
slider_B.oninput = function() {number_B.value = slider_B.value; setB(slider_B.value);};
number_B.oninput = function() {slider_B.value = number_B.value; setB(number_B.value);};
slider_F.oninput = function() {number_F.value = slider_F.value; setF(slider_F.value);};
number_F.oninput = function() {slider_F.value = number_F.value; setF(number_F.value);};
var count = true; // system analysis var v = 0; // speed of a mass
var rw = canvas.width / 30; var rh = canvas.height / 1.5; var x0 = 15 * rw - rw / 2; var y0 = rh / 1.33 - rh / 2;
// spring settings var coil = 10; // number of turns var startX = 0; // spring fastening
// create a rectangle (mass)
var rect = {
x: x0, width: rw,
y: y0, height: rh,
fill: "rgba(0, 0, 255, 1)" // colour
};
// capture a rectangle with the mouse
var mx_; // buffer position of the mouse (to calculate the speed of the ball when released)
document.onmousedown = function(e) { // function by pressing the mouse button
var m = mouseCoords(e); // we get estimated coordinates of the mouse cursor
var x = rect.x;
var xw = rect.x + rect.width;
var y = rect.y;
var yh = rect.y + rect.height;
if (x <= m.x && xw >= m.x && y <= m.y && yh >= m.y) {
if (e.which == 1) { // left mouse button is pressed
rect.xPlus = rect.x - m.x; // cursor shift relative to the cargo on the x
rect.yPlus = rect.y - m.y; // cursor shift relative to the cargo on the y
mx_ = m.x;
count = false;
document.onmousemove = mouseMove; // while a key is pressed, fanction of motions is correct
}
}
};
document.onmouseup = function(e) { // function when you release the mouse button
document.onmousemove = null; // when the key is released, no movement function
count = true;
};
function mouseMove(e) { // function when you move the mouse, it works only while holding LKM
var m = mouseCoords(e); // we get estimated coordinates of the mouse cursor
rect.x = m.x + rect.xPlus;
// v = 6.0 * (m.x - mx_) / dt / fps; // inertia preservation
v = 0;
mx_ = m.x;
}
function mouseCoords(e) { // function returns the calculated coordinates of the mouse cursor
var m = [];
var rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
m.x = (e.clientX - rect.left);
m.y = (e.clientY - rect.top);
return m;
}
// plot
var vGraph = new TM_graph( // determine the plot
"#vGraph", // on html-element #vGraph
250, // the number of steps by "x" axis
-1, 1, 0.2); // min value of Y-axis, max value of Y-axis, Y-axis step
function control() {
calculate();
draw();
requestAnimationFrame(control);
}
control()
// setInterval(control, 1000 / fps); // start of the system
function calculate() {
if (!count) return;
for (var s=1; s<=spf; s++) {
var f = -B*v - C * (rect.x - x0) - C1*Math.pow(rect.x - x0,3)+2*F*Math.sin(t);
v += f / m * dt;
//console.log(f);
rect.x += v * dt;
t+= dt;
steps++;
if (steps % 80 == 0) vGraph.graphIter(steps, (rect.x-x0)/canvas.width*2); // infeed graph data
}
}
function draw() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, w, h);
draw_spring(startX, rect.x, h/2, 10, 50);
ctx.fillStyle = "#0000ff";
ctx.fillRect(rect.x, rect.y, rect.width, rect.height);
}
function draw_spring(x_start, x_end, y, n, h) {
ctx.lineWidth = 2;
ctx.strokeStyle = "#7394cb";
var L = x_end - x_start;
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var x_st = x_start + L / n * i;
var x_end = x_start + L / n * (i + 1);
var l = x_end - x_st;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.bezierCurveTo(x_st, y, x_st + l / 4, y + h, x_st + l / 2, y);
ctx.bezierCurveTo(x_st + l / 2, y, x_st + 3 * l / 4, y - h, x_st + l, y);
ctx.stroke();
}
}
}